
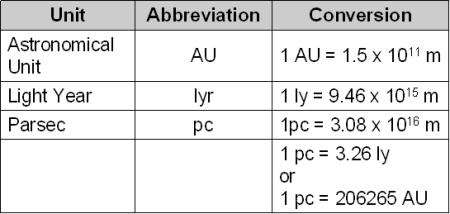
Example: hold a pen atĪrms length and alternate closing one eye at a time Sun so that the Earth- Sun distance were only 1Īrc-seconds across, the observer would be 1 parsec Means that if an observer were far enough away from Astronomical Unit (AU)Īn astronomical unit is the mean distance betweenĪ light-year is the distance light travels in 1Ī parsec is the distance a nearby object, 1 AUĪway "subtends" to one arc-second. Parsecs (for really distant galaxies - like the ones near the edge of the observable Universe, it is common to give distance in "redshift"). Seems to be more popular than using the parsec.įor very large distances, there are really threeĬhoices: astronomical units, light-years, and Not suffer the same confusion, but the light-year (kilometer, centimeter, millimeter, and so on) areĬommon place. Towards the metric system so variations on the meter Kilometers for the metric system and inches, feet,Īnd miles for the English system, distances toĭistant galaxies is given in light-years.Īs a rule of thumb, science tends to lean more That matter) in either centimeters, meters, and On Earth we measure distance (and dimensions for In astronomy, distances can be very large. Time in relation to Relativity is another matter - covered in the Cosmology section. With a phenomenon that occurred at hour 18 and 38 The right ascension (RA) coordinate of the Units of measure in time however, there can be someĬonfusion as time coordinates are a part of theĮquatorial measure of right ascension. Units of measure are: seconds, minutes, hours, Units of time is a simple matter, things occur inĪ linear fashion and so a value of time is assigned. Measure are applied: time, distance, mass and There are 4 categories in which standard of What standard unit of measure was to be used. Orbiter in 1999 was the result of confusion over The mathematics used in science, setting rules on Episode 10: Measuring Distance in the Universe.Physics - Concepts - Basic Units of Measure Still doesn’t make sense? Check out his episode of Astronomy Cast where we explain various methods astronomers use to measure the Universe.
#Parsec unit of measurement how to#
Here’s an article from NASA that explains how to derive the parallax measurement. The article explains how the astronomical unit might need to be changed as the Sun loses mass. We have written many articles about the parsec for Universe Today. If you put this into the calculation, you determine that Proxima Centauri is 1.295 parsecs away, or 4.225 light years. If you create a triangle, where one leg is the distance between the Earth and the Sun (one astronomical unit), and the opposite angle, measured by how far the star moves in the sky, is one arcsecond, the star will be 1 parsec away, the other leg of the triangle.įor example, the closest star in the sky, Proxima Centauri, has a parallax measurement of 0.77233 arcseconds – that’s how far it shifts in the sky from when the Earth shifts its position by 1 astronomical unit. Just a warning, you’re going to need to dust off your trigonometry for this. So, to put those terms together, a parsec is the parallax of one arcsecond. So astronomers measure the size of objects, or the parallax movement of stars in degrees, arcminutes and arcseconds. An arcminute is 1/60th of a degree, and an arcsecond is 1/60th of an arcminute.
#Parsec unit of measurement full#
Each slice is about twice the width of the full moon. Imagine the horizon around you broken up into 360 slices, or degrees.
In this instance, we’re not referring to a measure of time.

Now for the second part of “parsec”: arcsecond. Nearby stars will have shifted a tiny amount compared to more distant stars, and sensitive instruments can detect the change. Astronomers measure parallax by measuring how distant stars shift back and forth as the Earth travels around the Sun.Īstronomers measure the position of the stars at one time of the year, when the Earth is at a position in its orbit around the Sun, and then they measure again 6 months later when the Earth is on the other side of its orbit. Likewise, two different people, in two different parts of the world, might see the exact same event in the sky or outer space yet, it might appear entirely different due to their locations. Since you are in a different place, facing a different direction, they appear to be in different places. If you go across the street and look at the same houses from your neighbor’s backyard, they will be on the opposite sides. For example, if you stand on your porch and look across the street, you will see a house on your left and a house on your right.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
